Tbb多线程笔记
1.tbb用来做什么
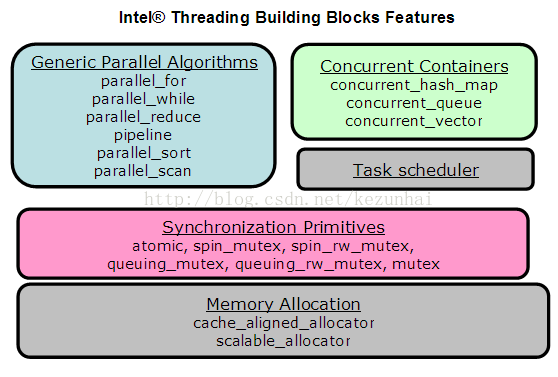
TBB(Thread Building Blocks),获得过 17 届 Jolt Productivity Awards,是一套 C++ 模板库,和直接利用 OS API 写程序的 raw thread 比,在并行编程方面提供了适当的抽象,当然还包括更多其他内容,比如 task 概念,常用算法的成熟实现,自动负载均衡特性还有不绑定 CPU 数量的灵活的可扩展性等。
TBB中提供了 parallel_for、parallel_while、 parallel_reduce等;(这些是TBB给C++程序员的比较高层的接口)并行肯定是多线程,这样的话数据竞争问题就比较棘手,所以TBB提供并发容器;如果觉得 TBB提供的这些接口还没有办法解决性能问题,那就可以更深入的研究使用mutex、atomic、task等。
由底层到高层,task_scheduler——–concurrent_container——–parallel_for—pipeline 简单说,TBB帮我们调度一个个task(比OS的调度要高效),实现高效的并行算法。
2.下载安装
下载地址:
安装: 官网上有一个TBB的插件,有VS版本的,可以下载下来,按说明装一下。
VS的工具->选项->环境->外接程序/宏的安全性,将你对应VS版本的目录添加上去。
在VS中右键项目,选择tbb->TBB版本,工具可以实现自动将TBB包含目录与库目录,加到项目上。

3.使用
1)、parallel_for 适用场合:多个数据或请求彼此没有依赖关系,所要进行的操作是一样的(典型SPMD)
template<typename Range , typename Body >
void parallel_for (const Range &range, const Body &body)
range,用来定义系列,下面是模板,可以用STL容器
R::R( const R& );
R::~R();
bool R::is_divisible() const; //True if range can be partitioned into two subranges
bool R::empty() const;// True if range is empty
R::R( R& r, split ); //Split range r into two subranges.
body,用来执行操作的定义类,用户定义,下面是模板
Body::Body( const Body& );// Copy constructor
Body::~Body();
//Function call operator applying the body to range r.
void Body::operator()( Range& r ) const;
例子:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <tbb/tbb.h>
#include <tbb/blocked_range.h>
#include <tbb/parallel_for.h>
using namespace std;
using namespace tbb;
typedef vector<int>::iterator IntVecIt;
//定义操作
struct body
{
void operator()(const blocked_range<IntVecIt>&r)const
{
for(auto i = r.begin(); i!=r.end(); i++)
{
cout<<*i<<' ';
}
}
};
int _tmain(int argc, _TCHAR* argv[])
{
vector<int> vec;
for(int i=0; i<10; i++)
{
vec.push_back(i);
}
//执行操作
while (1)
{
parallel_for(blocked_range< IntVecIt>(vec.begin(), vec.end()), body());
cout<<"sleep...\n";
Sleep(100);
}
return 0;
}
2)、parallel_reduce 适合于需要汇总的情况,即各个数据的结果需要汇总回来
有两种形式: 一种是lamda形式,一种是Body形式
Body定义
Body::Body( Body&, split ); //Splitting constructor.
//Must be able to run concurrently with operator() and method join
Body::~Body();
void Body::operator()( Range& r );
void Body::join( Body& b ); //Join results.
其中一种lambda的:
template<typename Range , typename Value , typename RealBody , typename Reduction >
Value tbb::parallel_reduce (
const Range & range,
const Value & identity,
const RealBody & real_body,
const Reduction & reduction
)
lambda的实例:
int result = parallel_reduce(
blocked_range<vector<int>::iterator>(vec.begin(), vec.end()),
0,
[](const blocked_range<vector<int>::iterator>& r, int init)->int{
for(auto a = r.begin(); a!=r.end(); a++)
init+=*a;
return init;
},
[](int x, int y)->int{
return x+y;
}
);
cout<<"result:"<<result<<endl;
3)、parallel_while 有时不知道循环何时结束,即使用for的end未知,在这种情况下可以使用parallel_while
4)、并发容器:concurrent_hash_map\concurrent_vector\concurrent_queue
参考: